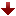
<xml version = "1.0" ?>
<DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd">
<-- setting dimension box and text alignment -->
<html xmlns = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title> Simple Box Dimension</title>
<style type="text/css">
div { background-color: #ffccff;
margin-bottom: .5em }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="width: 20%">Here is some text that goes
in a box which is set to stretch across twenty percent of
the width of the screen.</div>
<div style="width: 80%; text-align: center">
Here is some CENTERED text that goes in a box
which is set to stretch across eighty percent of
the width of the screen.</div>
<div style="width: 20%; height: 30%; overflow: scroll">
This box is only twenty percent of the width and thirty percent
of the height. what do we do if it overflows? Set the overflow
property to scroll!</div>
</body>
</html>
The inline style in the First div, illustrates how to set the width of an element on screen; here, we indicate that the DIV should occupy 20% of the screen width. Most elements are left-aligned by default; however, this alignment can be altered to position the element elsewhere. The height of an element can be set similarly, using the height property. The height and width values also can be specified as relative or absolute lengths. For Example
width : 10em
Sets the element’s width to be equal to 10 times the font size. The Second div sets text in the element to be center aligned; other values for the text-aligned property include left and right.
One problem with setting both dimensions of an element is that the content inside the element can exceed the set boundaries, in which case the element is simply made large enough for all the content to fit. However, in the Third div, we set the overflow property to scroll, a setting that adds scrollbars if the text overflows the boundaries.
Source → Deitel – 3rd Edition